Git internals book
This morning I saw at my rss feed that a book called Git Internals by Scott Chacon has been opensourced. So, having an idle afternoon, I borrowed an ebook from a relative and read it while taking a sunbath (idea! Have a tablet with a electronic ink screen and vim, and program on the beach.. I’m eager to see fast enough e. ink for that!)
The first 10-15 pages of the book are about the internal cogs of git, and they are easy to read and very well explained with diagrams. I invite you to read them, because thanks to them I now understand Git very well. The rest of the book covers how to work with git, and typical commands. Some of its bits are new to me, so I have summarized them here for you and me (well, mostly for me, I doubt anyone is reading this :P).
Possible workflows for decentralized SCM systems as git
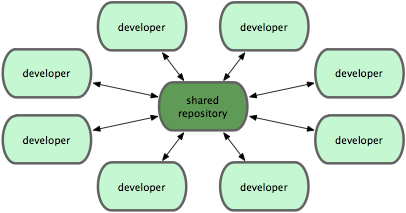
- Central repository model: better for small teams.
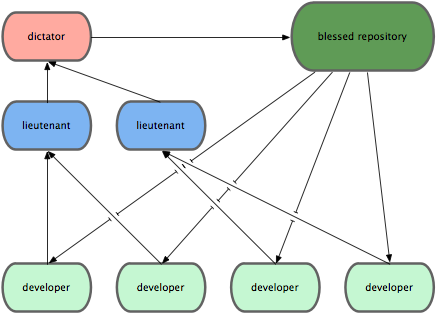
- Dictator and leutenant model: better for large teams. Eg: Linux kernel
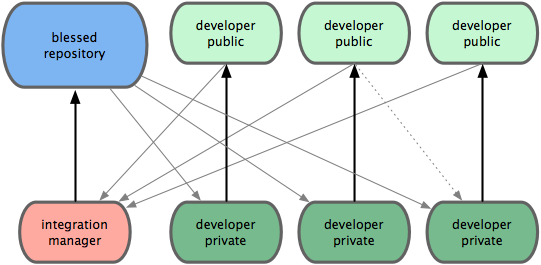
- Integration manager model: community based git repos. Eg: Github
GUIs that come bundled with git
Provide simple visualization of git trees and commits:
-
gitk: Tcl/Tk based browser. Will take most of the same arguments that git log will take.
-
git instaweb: Without Tk. It fires up a web server running the gitweb CGI script, using lighttpd, apache, or webrick and then opens your default browser.
-
Open:
git instaweb --httpd = lighttpd or apache or webrick -
Close:
git intaweb stop
-
Crypto signed tags
-
Sign tag:
git tag -s(sign with email address GPG key)or
git tag -u <keyID> v1.0 -m "release v1.0" -
Verify signed tag:
git tag -v v1.0 -
push tag to remote:
git push origin [tagname]
###Caring of git From time to time, you need to take care of git repos, usually the big ones. To have them healthy and running quickly:
-
Garbage collection:
git gc(it is possible to turn it off and on automatically). -
Fsck:
git fsck: To know if there are unreachable or corrupted objects in the DB and fix them.git prune: To remove dangling objects.
Sharing repos
It is done using the git-daemon, which supports these 3 protocols:
-
git: No built in integration, generally you cannot push over it.
-
ssh: If an user has ssh and write access, that user can push.
-
http: easy setup, you need just static web server. But to push, you need to run a DAV server.
Browse git objects(blobs) directly
-
git show [object] -
git cat-file [object]
Generating patch files
-
Generate:
git diff master..experiment > patchFile -
Apply patch:
patch -p1 patchFile patching file fileToPatch
Export a tree
git-archive: For exporting a snapshot of a git tree.
Interactive shells
git add -i: Provides an interactive shell to select files, and
also allows to commit only chunk of files (useful for a patch).
git rebase -i: For complex rebasing.
Víctor Cuadrado Juan
I'm Víctor Cuadrado Juan, a developer and FOSS enthusiast, in love with Linux. Currently living in Nürnberg, Germany. Feel free to waste your precious time around here, or to contact me.